1 Reproduction
1.1 Inheritance of genes
gene은 유전의 단위이고 DNA의 조각들로 이루어져 있다. gametes를 통해 다음 세대로 전달되며 대부분의 DNA는 chromosome으로 응축되어 있다. 인간에게는 체세포 핵 내에 46개의 chromosome이 있다. (gametes와 그들의 precursor 제외) chromosome에서 특정 trait에 대한 유전자의 위치는 locus
1.2 Comparsion of Assexual and Sexual Reproduction
1.2.1 Assexual Reproduction
gametes의 결합으로 zygote를 형성하지 않고 자신의 gene을 모두 전달한다. 한 개체로 부터 생긴 다른 개체 또는 그룹은 부모와 유전적으로 동일하다.
1.2.2 Sexual Reproduction
두 개체에서 상속된 gene을 통해 고유한 조합의 유전자를 가진 후손이 생긴다.
1.2.2.1 Human Cell
인간의 체세포에는 23쌍의 homologous chromosome(homolog)이 있다. homologous pair는 길이, centromere의 위치, staining pattern 등이 동일하고, 같은 형질을 조절하는 gene을 포함하고 있다. sex cchromosome을 제외한 나머지 22쌍의 chromosome pair를 autosome이라고 부른다.
1.2.2.1.1 Meiosis
DNA 합성이 일어나는 세포에서 각 chromosome이 복제된다. 복제된 chromosome은 2개의 동일한 sister chromotid로 구성된다. 난자의 sex chromosome은 X, 정자의 sex chromosome은 X 또는 Y이다.
1.2.3 Sexual Life Cycle
meiosis와 fertilization의 전환은 대부분의 유기체에서 공통적으로 나타난다. meiosis는 diploid cell에서만 나타난다.
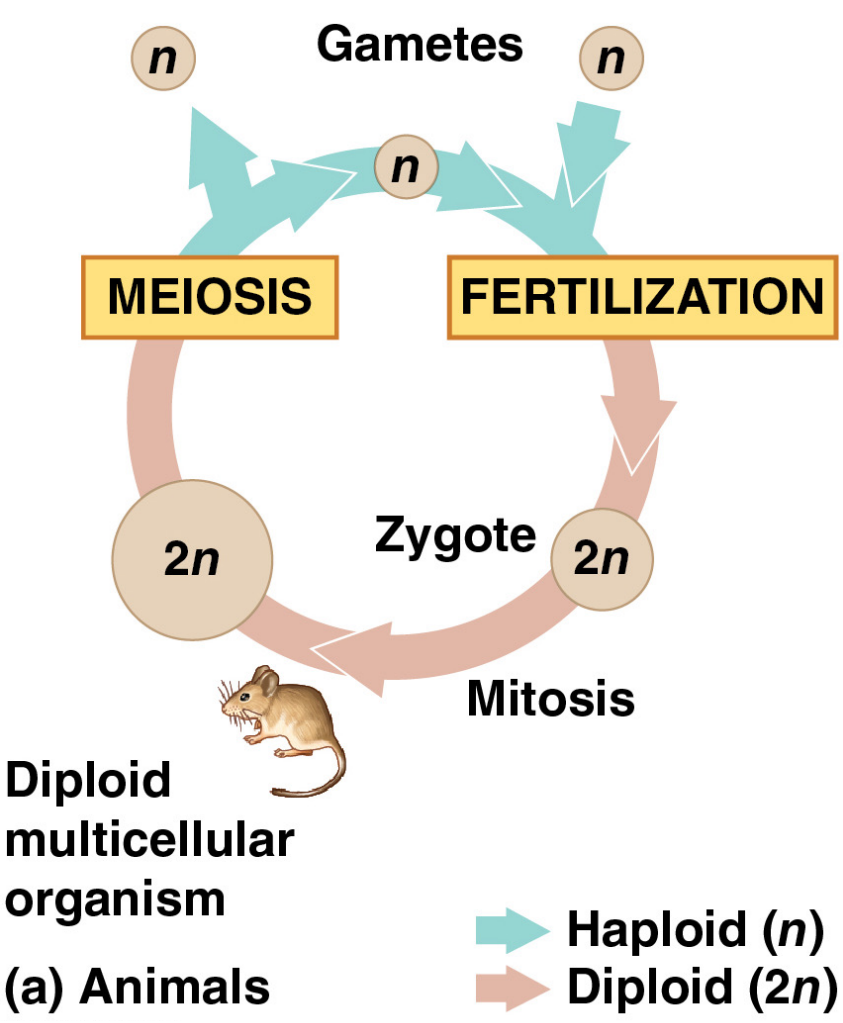
1.2.3.1 Animals
대부분의 동물에서 gametes는 haploid이다. gametes는 meiosis에 의해 생성되며 fertilization이 일어날 때 까지 더 이상 mitosis를 하지 않는다.
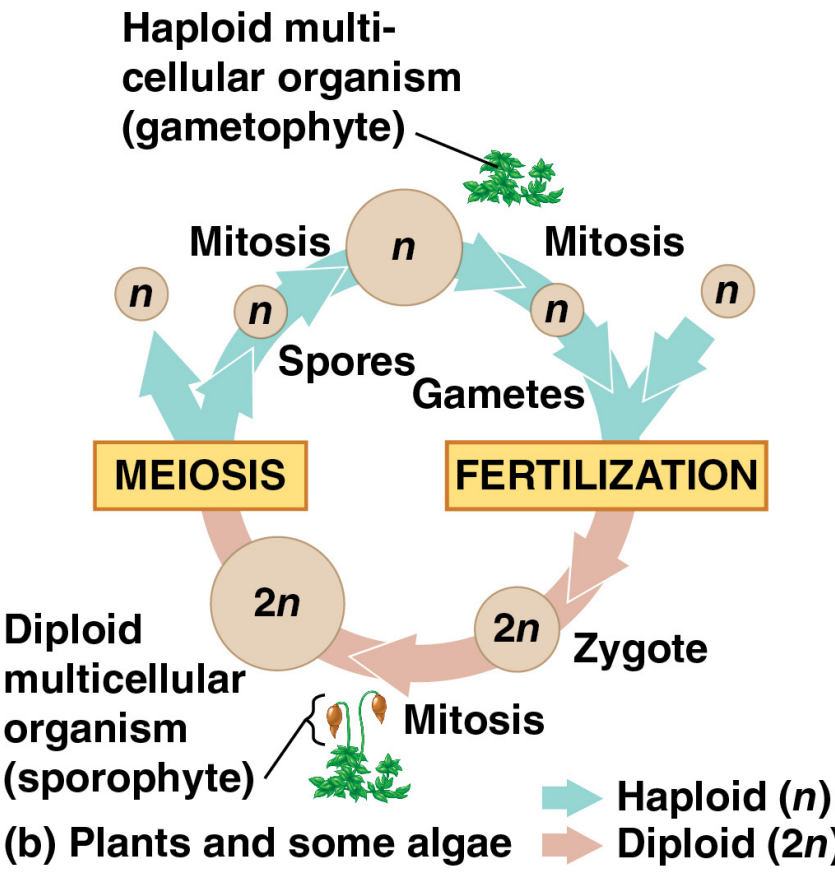
1.2.3.2 Plants
식물들과 일부 조류에서는 alternation of generatuin이 나타난다. 여기에는 diploid와 haploid multicellular stage로 이루어진다. diploid organism은 sporophyte라고 부르며 meiosis를 통해 haploid spore를 생성한다. sprore는 mitosis를 통해 gametophyte라고 불리는 haploid organism으로 성장한다. gametophyte는 다시 mitosis를 통해 haploid gamete를 생성하고 gametes 간의 수정을 통해 diploid sporophyte를 형성한다.
 7
7
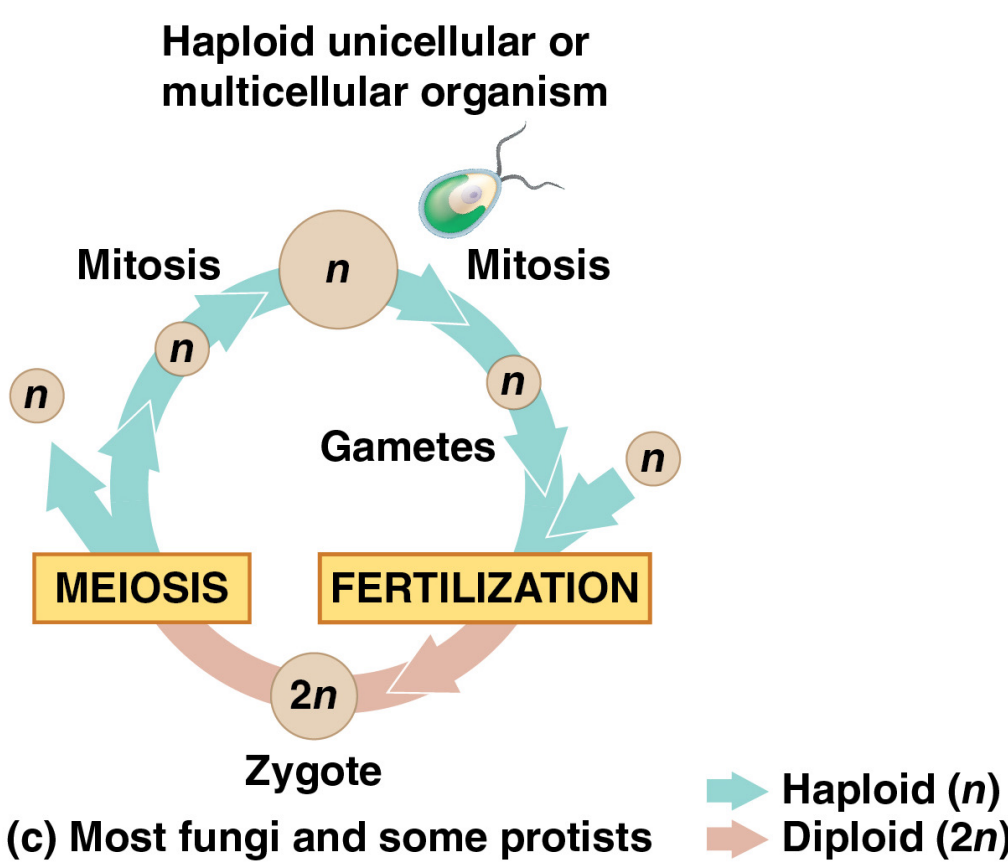
1.2.3.3 Fungi
대부분의 fungi와 일부 prosist에서는 multicellular diploid stage가 없으며 유일한 diploid stage는 single celled zygote이다. zygote는 meiosis를 통해 haploid cell을 생성한다. haploid cell은 mitosis를 통해 haploid multicelluler organism을 형성한다. 성체 haploid는 mitosis를 통해 gametes를 형성한다.
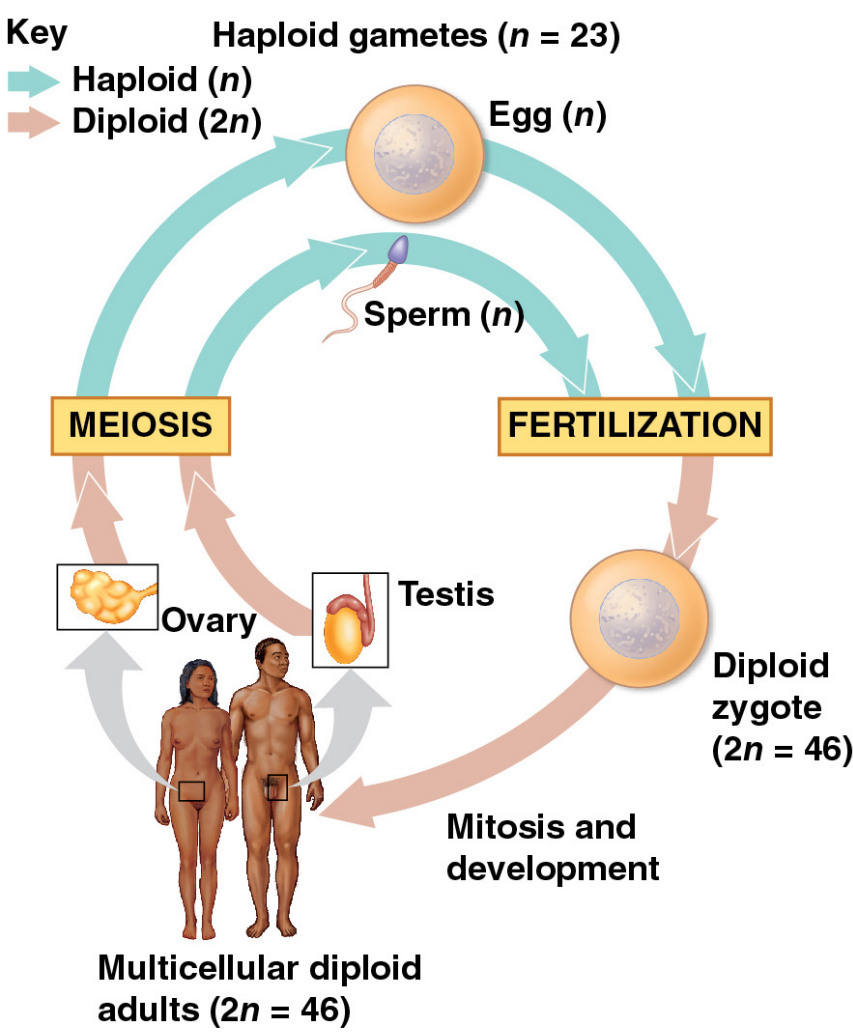
1.2.3.4 Human
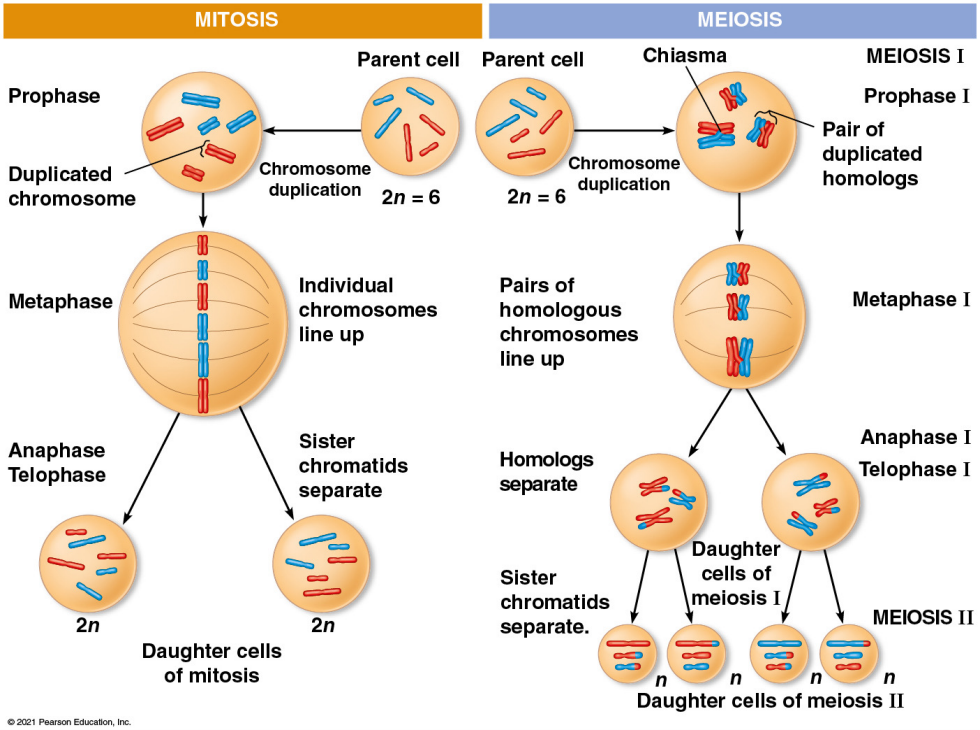
mitosis과 마찬가지로, meiosis에는 chromosome의 복제가 선행된다. 복제된 sister chromatid는 cohesin에 의해 매우 가까이 붙어있으며 이를 sister chromatid cohesion이라고 부른다. meiosis I과 meiosis II에서 일어나며 그 결과로 mitosis에서 2개의 딸세포를 형성하는 것과 달리 4개의 딸세포를 형성한다. sister chromatids는 4개의 haploid 딸세포에 분배된다.
1.3 Meiosis
1.3.1 Meiosis I
1.3.1.1 Prophase I
prophase 초기에 각각의 chromosome는 그 homolog와 쌍을 이루고 교차가 발생한다.
Crossing Oer and Synapsis During Prophase I interphase 이후, sister chromatids가 cohesin이라는 단백질에 의해 접합된다. nonsister chromatids는 접합점에서 정확하게 분리된다. 지퍼와 비슷한 구조를 가진 synaptonemal complex가 homologs를 붙잡는다. synapsis 동안 DNA가 끊어지고 다시 연결되어 nonsister chromatid 간의 교차가 일어난다.
1.3.1.2 Metaphase I
homolog의 쌍이 metaphase plate로 정렬되고 각 chromosome이 양극을 향한다. 양극으로 부터 온 microtubule이 chromosome의 kinetochore에 연결된다.
1.3.1.3 Anaphase I
homologous chromosome pair가 분리된다. pair의 chromosome은 spindle에 의해 서로 다른 극을 향하여 이동한다. sister chromatids는 centromere에서 붙어있는 상태로 극을 향해 이동한다.
1.3.1.4 Telophase I & Cytokinesis
telophase I 초기에 각 세포의 절반은 복제된 haploid chromosome set을 가지고 있다. 각각의 chromosome은 두 개의 chromatid로 구성되어 있다. cytokinesis는 일반적으로 동시에 일어나 두 개의 딸세포를 형성한다. 동물 세포에서는 cleavage furrow를, 식물 세포에서는 cell plate를 형성한다.
1.3.2 Meiosis II
1.3.2.1 Prophase II
prophase II에서 spindle apparatus가 형성된다. prophase II 후기에 2개의 chromatid로 구성된 chromosome들은 metaphase plate로 이동한다.
1.3.2.2 Metaphase II
metaphase II에서 sister chromatid가 metaphase plate에 배열된다. meiosis I에서의 cross over로 인해, 각 chromosome의 sister chromatids는 더 이상 유전적으로 동일하지 않다. sister chromatid의 kinetochore은 서로 다른 극으로부터 온 microtubules에 부착된다.
1.3.2.3 Anaphase II
sister chromatids가 분리된다. 각 chromosome으로 부터 분리된 sister chromatids는 이제 새로운 개별적인 chromosomes 처럼 서로 다른 극으로 이동한다.
1.3.2.4 Telophase II & Cytokinesis
chromosome이 양극에 도달한다. 핵이 형성되고, chromosome이 decondensing 되기 시작한다. cytokinesis가 cytoplasm을 분리 시킨다. meiosis가 끝날 때, 복제되지 않은 haploid chromosome set을 가진 4개의 딸 세포가 있다. 각 딸 세포는 부모 세포 또는 다른 딸 세포들과 유전적으로 구분 가능하다.
1.4 Comparsion of Mitosis and Meiosis
mitosis는 모세포 유전적으로 동일한 두 개의 세포를 형성하면서 chromosome set의 수를 줄인다. meiosis는 모세포 및 딸 세포끼리 유전적으로 다른 4개의 세포를 형성하면서 chromosome set의 수를 두 개에서 한 개로 줄인다. (2n n)
다음 3가지 사건은 meiosis I에서만 일어난다.
- prophase I의 synapsis와 crossing over: homologous chromosome은 물리적으로 연결되어 있고 유전적 정보를 교환한다.
- homologous pair가 methaphase plate에 정렬된다.
- anaphase I에서 homologs가 분리된다. sister chromatid cohesion은 sister chromatids가 meiosis I 동안 붙어 있도록 한다. mitosis에서 metaphase가 끝날 때 cohesin이 쪼개진다. meiosis의 anaphase I에서 homologs를 연결하던 cohesin이 분리되고 anaphase II에서 centromere의 cohesin이 분리된다. (anaphase I: homologs 분리, anaphase II: sister chromatids 분리)
1.5 Genetic Variation
1.5.1 Independent Assortment of Chromosomes
chromosome의 homologous pair은 meiosis의 metaphase I에서 랜덤하게 배열된다. independent assortment에서, 부모로 부터 받은 각각의 chromosome pair는 서로 다른 daughter cell로 들어가게 된다. chromosome pair가 독립적으로 분배됨을 통해 다양한 조합이 가능해진다.
1.5.2 Crossing Over
crossing over는 부모로 부터 받은 DNA가 재조합된 chromosome을 형성한다. 이는 두 부모로 받은 단일 chromosome의 DNA를 조합하여 유전적 다양성에 기여한다.
1.5.3 Random Fertilization
random fertilization은 어떤 정자든 난자에 융합할 수 있음을 통해 유전적 다양성을 증가시킨다.